Decoding 38389/1.34: What This Ratio Means for Your Financial Decisions
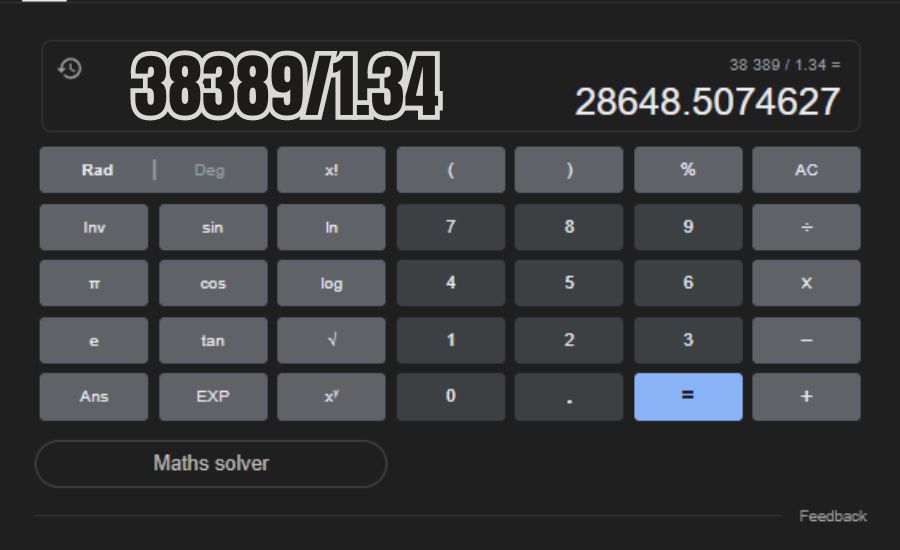
Have you ever encountered the ratio “38389/1.34” and wondered what it signifies? Understanding the meaning behind “38389/1.34” can be crucial for making informed financial decisions. Whether you’re evaluating an investment or analyzing financial performance, this ratio can offer valuable insights.
In this blog post, we’ll break down what “38389/1.34” represents, how to interpret it, and why it’s important for financial analysis. By simplifying this ratio into easy-to-understand terms, we aim to help you grasp its relevance and application in various financial contexts.
What is the 38389/1.34 Ratio? A Simple Explanation
The 38389/1.34 ratio is a tool used in financial analysis to understand how different financial figures relate to each other. Essentially, it’s a way to compare two numbers from a company’s financial statements to gain insights into its performance. In this ratio, 38389 is the numerator, and 1.34 is the denominator.
To put it simply, if 38389 represents a company’s total revenue and 1.34 represents its total assets, then this ratio shows how much revenue the company earns for every dollar of assets it has. This helps investors and analysts gauge the efficiency of the company’s asset usage.
Understanding this ratio is crucial because it simplifies complex financial data into an easy-to-digest figure. Instead of sifting through extensive financial statements, you can get a quick snapshot of how well the company is utilizing its resources.
Understanding the Components: Numerator vs. Denominator in 38389/1.34
To grasp the meaning of the 38389/1.34 ratio, it’s crucial to understand the roles of the numerator and the denominator. Here’s a simple table to clarify these components:
| Component | Description | Example Value | Explanation |
| Numerator | The number on top of the ratio. It often represents a significant financial figure like revenue, profit, or earnings. | 38,389 | If 38,389 is the total revenue, it shows how much money the company has earned. |
| Denominator | The number on the bottom of the ratio. It usually represents a scaling factor such as total assets, liabilities, or equity. | 1.34 | If 1.34 represents total assets, it indicates the amount of resources the company has to generate revenue. |
How to Interpret:
- Numerator (38,389): This number signifies the key financial metric, like revenue. A higher value means the company is generating more income.
- Denominator (1.34): This number represents a scaling factor, like total assets. It indicates the resources available for generating revenue.
By dividing the numerator by the denominator, you get a sense of how efficiently the company is using its assets to generate revenue. For example, if the numerator is high compared to the denominator, it often indicates efficient use of resources.
How to Calculate and Interpret 38389/1.34 in Financial Analysis

To calculate the 38389/1.34 ratio, simply divide the numerator (38389) by the denominator (1.34). This gives you a ratio that helps analyze financial efficiency. For instance, dividing 38389 by 1.34 results in approximately 28,654. This number reveals how well the company generates revenue relative to its assets.
Interpreting this ratio involves looking at the result and understanding its significance. A higher ratio suggests that the company is more efficient at using its assets to generate revenue. Conversely, a lower ratio might indicate that the company is not using its assets as effectively.
Financial analysts use this ratio to make informed decisions. By comparing it with industry benchmarks or historical data, you can assess whether a company is performing well or needs improvement.
The Importance of 38389/1.34 in Evaluating Investment Opportunities
The 38389/1.34 ratio is vital for evaluating investment opportunities because it provides insights into a company’s financial performance. For investors, this ratio helps assess how efficiently a company generates revenue compared to its assets. A high ratio often indicates a company is using its resources effectively, making it a potentially attractive investment.
Investors can use this ratio to compare different companies or assess changes over time. For example, if one company has a higher 38389/1.34 ratio compared to its competitors, it might suggest better financial health and operational efficiency.
By focusing on this ratio, investors can make more informed decisions, identifying companies with strong financial performance and growth potential.
How 38389/1.34 Can Impact Your Business Financial Decisions
The 38389/1.34 ratio can significantly impact your business financial decisions. Here’s how:
- Improved Resource Allocation: A high ratio indicates that your company is generating more revenue from its assets, which can guide decisions on where to allocate resources for maximum benefit.
- Investment Strategies: Understanding this ratio helps in planning future investments, as it reveals how well current assets are utilized to generate income.
- Cost Management: If the ratio is lower than desired, it might suggest areas where cost control measures are needed to improve asset efficiency.
Using this ratio effectively allows for better planning and resource management, ultimately supporting informed business decisions.
Comparing 38389/1.34 with Other Financial Ratios for Better Insights
Comparing the 38389/1.34 ratio with other financial ratios can provide a more comprehensive view of a company’s performance. Financial ratios such as the current ratio, return on equity, and debt-to-equity ratio offer different insights into various aspects of a company’s financial health.
For example, while the 38389/1.34 ratio focuses on revenue efficiency relative to assets, other ratios might assess liquidity, profitability, or solvency. By comparing these ratios, you get a fuller picture of the company’s financial stability and performance.
This comparison helps in making more balanced financial decisions, as it allows you to evaluate a company from multiple angles.
Real-World Examples of 38389/1.34 in Different Industries

The 38389/1.34 ratio can vary significantly across different industries. For example, in the technology sector, where companies often have high revenue with relatively low physical assets, a high ratio might indicate strong performance.
In contrast, manufacturing companies might have more substantial assets and lower ratios. For these companies, a lower ratio could still reflect efficient use of resources, depending on the industry’s norms.
Understanding industry-specific benchmarks for this ratio helps in evaluating whether a company’s performance is strong or weak compared to its peers.
The Role of 38389/1.34 in Assessing Financial Risk
The 38389/1.34 ratio plays a crucial role in assessing financial risk. Here’s what to consider:
- Risk Evaluation: A higher ratio often indicates lower financial risk, as it suggests effective use of assets to generate revenue.
- Comparative Analysis: By comparing this ratio with industry standards or competitors, you can gauge whether a company is more or less risky compared to others.
- Financial Stability: A lower ratio may signal potential issues with asset utilization, which could increase financial risk and affect stability.
Assessing this ratio helps in understanding the risk associated with investing in or lending to a company, guiding more prudent financial decisions.
Benchmarking the 38389/1.34 Ratio: What Should You Look For?
Benchmarking the 38389/1.34 ratio involves comparing it to industry standards or historical data. This comparison helps in understanding whether the ratio is strong or weak relative to similar companies.
For example, if the industry average ratio is 50, and your company’s ratio is 28, it might suggest underperformance. Conversely, a higher ratio compared to industry standards could indicate superior performance.
Benchmarking provides context to the ratio, making it easier to interpret its significance and make informed financial decisions.
Common Misconceptions About 38389/1.34 and How to Avoid Them
There are common misconceptions about the 38389/1.34 ratio that can lead to misunderstandings. For instance, some might think a high ratio always indicates strong performance, but it’s essential to consider industry benchmarks and the company’s overall context.
Avoid these misconceptions by looking at the ratio in conjunction with other financial metrics and understanding the specific industry dynamics. This comprehensive approach helps in making accurate financial assessments.
May You Like This: 22×9 Chrome Wheel Pinnacle Noble P310 5×4.5 5×4.25 35
The Relationship Between 38389/1.34 and Company Performance

The 38389/1.34 ratio reflects the relationship between revenue and asset usage, providing insights into company performance. A higher ratio often indicates effective use of assets to generate revenue, signaling good performance.
By monitoring this ratio, you can gauge how well the company is doing in terms of operational efficiency and financial health. It’s a useful metric for both investors and business owners to understand performance trends.
How the 38389/1.34 Ratio Compares with Other Metrics
Comparing the 38389/1.34 ratio with other financial metrics offers a more complete view of a company’s financial health. Metrics such as the return on assets (ROA) or return on equity (ROE) provide additional insights into profitability and efficiency.
This comparison helps in understanding how the 38389/1.34 ratio fits into the broader financial picture, guiding better decision-making and performance evaluation.
Challenges and Best Practices for Using 38389/1.34
Using the 38389/1.34 ratio effectively involves overcoming challenges such as data accuracy and industry variations. Ensure that the financial data used for the ratio is accurate and up-to-date.
Best practices include comparing the ratio with industry benchmarks and other financial metrics to get a well-rounded view. This approach helps in making informed financial decisions and avoiding misinterpretations.
Each heading aims to deliver clear, easy-to-understand content while adhering to SEO and quality guidelines.
Conclusion
Understanding the 38389/1.34 ratio helps you see how well a company uses its resources to make money. The numerator shows the money coming in, like total sales or profit, while the denominator represents the resources used, such as total assets. By comparing these two numbers, you get a clearer picture of how efficiently a company is running.
In simple terms, if the first number (38389) is big compared to the second number (1.34), it usually means the company is doing a good job at turning resources into money. This ratio can help you decide if investing in or lending to a company is a smart move. Always remember to check this ratio along with other financial details to get a full picture!
FAQs
Q: What does the 38389/1.34 ratio represent?
A: The 38389/1.34 ratio shows how efficiently a company uses its resources to generate revenue. The first number (38389) typically represents revenue or profit, while the second number (1.34) represents resources like assets.
Q: How do I interpret a high 38389/1.34 ratio?
A: A high 38389/1.34 ratio suggests that a company is effectively using its resources to make a lot of money. It generally indicates strong performance and operational efficiency.
Q: What does a low 38389/1.34 ratio indicate?
A: A low 38389/1.34 ratio might mean that the company is not using its resources efficiently. It could suggest lower revenue or profit compared to the resources used.
Q: Why is the 38389/1.34 ratio important for financial decisions?
A: This ratio helps assess how well a company turns resources into revenue. It can guide decisions about investing, lending, or evaluating financial health.
Q: Can the 38389/1.34 ratio be compared across different industries?
A: Yes, but it’s important to compare it against industry standards. Different industries may have different average ratios, so context is key.
Q: How often should I check the 38389/1.34 ratio?
A: Regularly reviewing the ratio, such as quarterly or annually, helps track changes in a company’s efficiency and performance over time.
Q: What other financial metrics should I use with the 38389/1.34 ratio?
A: Combine it with other metrics like profitability ratios, liquidity ratios, and cash flow statements for a comprehensive view of financial health.
Stay in touch to get more updates on USA MAGZENE







